Dr. Ruchi Verma
Assistant Professor
Department of Food Processing and Technology
Gautam Buddha University, Greater Noida-201312
Overview
In the 21st century, food waste has become a global challenge, affecting sustainability, economy, and nutrition security. Nearly one-third of all food produced globally about 1.3 billion tonnes is wasted annually, with fruits and vegetables constituting the largest share of this loss. This discarded biomass contains valuable nutrients, phytochemicals, and functional compounds that can be repurposed into health-oriented products. The concept of “From Waste to Wellness” emphasizes transforming food waste into functional beverages, aligning with the principles of a circular economy while promoting human health and environmental responsibility.
- Nutritional and Functional Potential of Food Waste
Food processing generates substantial by-products such as peels, seeds, pomace, and pulp residues. These materials, often discarded, are rich in bioactive compounds including phenolics, flavonoids, carotenoids, dietary fibers, and vitamins. Citrus peels, mango kernels, apple pomace, and pomegranate rinds are potent sources of antioxidants and antimicrobial agents. When these components are converted into functional beverages, they not only enhance nutritional profiles but also deliver physiological benefits like improved digestion, reduced oxidative stress, and better metabolic balance. Such compounds play a crucial role in combating chronic diseases, including obesity, cardiovascular disorders, and diabetes. For instance, phenolic-rich extracts from fruit peels can serve as natural functional ingredients that enhance the antioxidant capacity of juices, teas, or fermented drinks. Therefore, valorizing food waste enables both waste reduction and wellness promotion through health-enriched beverage formulations.
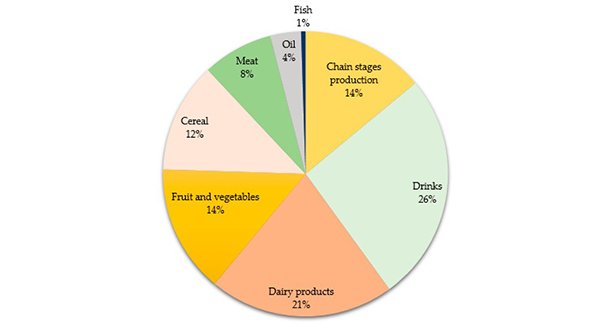
Figure 1. Production of agro-food waste in different industries (Source: Nayak et al., 2019)
- Techniques and Innovations in Beverage Development
The upcycling of food waste into functional beverages involves various sustainable extraction and formulation techniques. Technologies such as enzymatic hydrolysis, ultrasound-assisted extraction, and membrane filtration efficiently recover bioactives while preserving nutritional integrity. Fermentation using probiotics (e.g., Lactobacillus spp.) represents a promising approach, converting fruit residues into fermented probiotic drinks enriched with organic acids, peptides, and vitamins. For example, pineapple peel and core can be fermented to develop probiotic beverages with excellent sensory properties. Similarly, mango seed kernel extract can be blended into smoothies or dairy-free drinks to enhance antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. Apple pomace and grape skins serve as natural sources of fiber and anthocyanins, making them suitable for developing color-rich, health-boosting beverages. Furthermore, modern encapsulation technologies help stabilize sensitive compounds, ensuring extended shelf life and functionality.
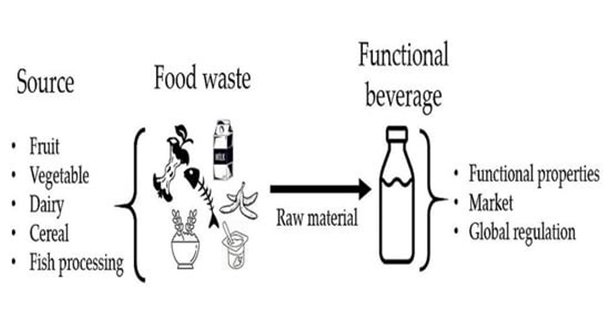
Figure 2. Food Waste as an Ingredient in Functional Beverages (Source: www.mdpi.com)
- Sustainability and Economic Impact
Upcycling food by-products into value-added beverages contributes significantly to sustainable food systems. It reduces burdens on landfills, curbs greenhouse gas emissions, and minimizes resource wastage during food production. Economically, it supports small and medium-scale enterprises to diversify their product lines affordably. Through innovative processing, what was once considered a cost of disposal can become a profitable health-oriented product range. In developing economies, this transformation introduces opportunities for rural entrepreneurship and community-level processing units. Local industries can harness agro-wastes like sugarcane bagasse, citrus pulp, or banana peels to produce low-cost, nutrient-dense drinks. This model not only promotes environmental sustainability but also strengthens local economies by converting agricultural residues into income-generating wellness products.
- Case Studies and Emerging Trends
Several successful case studies highlight how food waste is being turned into functional beverages globally. In India, researchers have formulated probiotic beverages from fruit pomace such as jamun, banana peel, and citrus waste. These drinks deliver both nutritional benefits and enhanced sensory appeal. Globally, start-ups are producing fruit peel-infused kombucha, vegetable pulp smoothies, and plant-based energy drinks sourced from surplus produce. Emerging trends emphasize zero-waste manufacturing, clean labeling, and consumer awareness regarding circular nutrition. Beverage industries are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning tools to optimize product formulation and quality consistency. Functional beverage prototypes now aim to combine health, sensory satisfaction, and environmental sustainability a triple-win outcome for producers and consumers alike.
- Challenges and Future Perspectives
While the focus on food waste valorization is growing, challenges remain. Standardization of extraction processes, regulatory compliance, and consumer acceptance are critical barriers to commercialization. Variability in composition and seasonal supply also pose formulation hurdles. Ensuring safety, stability, and sensory acceptance is essential before market introduction. Future research must explore integrated processing models combining fermentation, enzymatic treatment, and green extraction techniques like supercritical CO₂ and pulsed electric fields. Additionally, establishing safety guidelines and quality standards under national and international food regulations will facilitate broader commercialization. Collaboration between academia, industry, and policymakers is pivotal to developing large-scale production systems for functional beverages derived from food waste.
Conclusion
The transformation of food waste into functional beverages represents a practical synergy between nutrition, sustainability, and innovation. This approach exemplifies the shift towards circular economies where waste materials evolve into high-value health-promoting products. By adopting sustainable technologies and valorizing agricultural residues, industries can reduce environmental footprints while meeting the growing consumer demand for natural, health-oriented drinks. From waste to wellness, the upcycling of food by-products into functional beverages promises not just a healthier planet, but also a healthier future for humanity.
References
- Ullagaddi, R. (2025). Food waste upcycling and functional foods: Innovations for sustainability and health. African Journal of Biomedical Research, 28(1), 135-149.
- Lucarini, M., Durazzo, A., & Santini, A. (2021). Fruit wastes as a valuable source of value-added ingredients for developing functional foods and nutraceuticals. Foods, 10(10), 2344.
- Shirahigue, L. D., & Celegato, G. F. (2020). Agro-industrial wastes as sources of bioactive compounds for food industry applications. Ciência Rural, 50(4), e20190760.
- Ahmed, J., Tabassum, N., Ezzatullah, M., & Saleem, M. (2022). Valorization of fruit and vegetable waste for value-added functional beverages: A review. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 59(5), 1945-1958.
- Nayak, A.; Bhushan, B. An overview of the recent trends on the waste valorization techniques for food wastes. Environ. Manag.2019, 233, 352–370