The global spice oleoresin market is experiencing significant growth, driven by a surging demand for natural ingredients in the processed food and fragrance industries. Consumers’ increasing health consciousness has led to a preference for natural colouring and flavouring agents over artificial alternatives.
Spice oleoresins, which are highly concentrated liquid extracts of raw spices, offer a complete and consistent flavour profile, including both volatile and non-volatile constituents. These botanical extracts are obtained through a solvent extraction process, followed by solvent removal. Their advantages over traditional whole or ground spices are numerous: enhanced visual appeal, superior and consistent flavour, longer shelf life, cost-effectiveness, and ease of storage and transport due to their concentrated nature. They also boast a lower microbial load and can effectively replace traditional spices in most applications where the physical appearance or bulk of the spice is not crucial.
A Legacy of Innovation and Market Dominance
The commercialisation of spice oil and oleoresin extraction began in Germany in the early 20th century. India, however, has emerged as a global leader in this sector, controlling a remarkable 60% of the 13,500-tonne global spice oleoresin market. Pioneering efforts in India, such as the establishment of oleoresin manufacturing in 1969 by Kancor Ingredients (formerly Bombay Oil Industries), followed by companies like Synthite Industries and Plant Lipids, laid the groundwork for this dominance. Notably, the Indian extraction procedure, developed by the Central Food Technological Research Institute, is a unique two-stage process that effectively separates essential oils.
Key Indian players in this market include Synthite Industries, Plant Lipids, Kancor Ingredients, Venkatramna Industries, Silverline Chemicals Ltd, Agnes Herbs, Adani Pharmachem Private Limited, and Ozone Naturals. While India maintains a strong lead, China has emerged as a significant competitor, particularly in the paprika oleoresin segment.

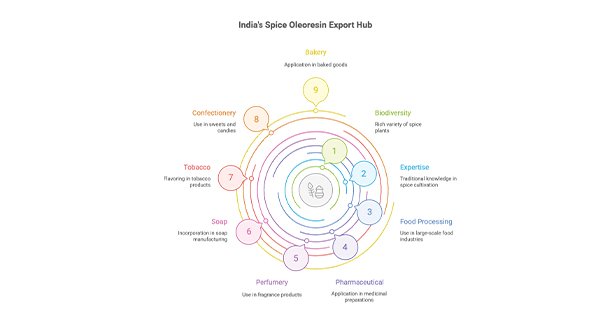
Diverse Applications Across Industries
Spice oleoresins are versatile and find extensive applications across various industries, serving as base flavours or components of complex flavour profiles. They can be used directly or blended to create a wide range of seasonings, flavours, and perfumes.
- Food and Beverage Industry: They are widely used as colouring agents in products like butter, meat, cheese, snacks, jellies, jams, poultry feeds, and frozen foods. They are also crucial in beverages, meat canning, confectionery, sauces, and as a base for numerous seasonings.
- Healthcare and Personal Care Industries: Their natural properties and consistent composition make them valuable in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and personal care products.
Key Oleoresins
Black Pepper Oleoresin: Derived from black pepper berries, this olive-green liquid offers the characteristic pungent taste and aroma of pepper due to its piperine and volatile oil content. Beyond its use in flavouring meat products and as a preservative, it’s gaining traction in traditional medicinal systems like Ayurveda for treating various ailments, including digestive issues and joint pains. The global market for black pepper oleoresin is experiencing significant growth driven by its diverse applications.
Paprika Oleoresin: Extracted from red paprika fruits, this oleoresin is a vital natural colouring and flavouring agent. Its colour comes from capsanthin and capsorubin, while capsaicin provides pungency. It’s extensively used to colour and flavour a wide array of food products, including meat products, confectionery, snacks, soups, sauces, and bakery items. The demand is particularly high in regions with a strong preference for clean-label natural ingredients.
Cardamom Oleoresin: Obtained from cardamom seeds, this extract is characterised by its sweet-spicy, warming fragrance. It’s broadly used as a domestic spice, a fragrance component, and a flavour compound in various dishes, sweeteners, and curry products. In pharmaceuticals, it’s recognised for treating digestive disorders and is also employed in personal care products and perfumes.
Market Growth and Future Outlook
The global spice oleoresin market is poised for steady growth. The market, valued at USD 1.44 billion in 2018, is projected to register a CAGR of 4.7% over the forecast period. This growth is fuelled by increasing consumption of processed meat, confectionery, and baked goods, as well as the rising demand for food additives and the proliferation of multi-cuisine restaurants worldwide.
Oleoresins’ superior properties—including uniform composition, consistent strength, absence of contaminants, ease of storage and transport, and longer shelf life—make them an increasingly attractive alternative to ground spices. Continuous research and development initiatives, particularly in introducing new varieties and improving quality for applications like aromatherapy, are expected to further augment market growth. As consumer demand for natural ingredients continues to rise, spice oleoresins are set to play an even more crucial role in shaping the flavours and colours of products across diverse industries.
In India, spice oleoresins are extensively utilised across various industries, primarily due to their concentrated form, consistent quality, extended shelf life, and superior hygienic standards compared to traditional raw or ground spices. Their most significant application lies within the food and beverage sector. Here, they are crucial as natural flavouring agents, imparting the authentic taste and aroma of various spices to a wide array of products. This includes processed foods like soups, sauces, dressings, and ready-to-eat meals, as well as meat and seafood products, confectionery, bakery items, dairy products, and snacks. Furthermore, they form the essential base for numerous compounded seasonings and ready-made spice blends, a growing segment in the Indian culinary landscape. Beyond flavouring, oleoresins like paprika and turmeric are widely employed as natural colouring agents in products such as butter, cheese, and various processed foods, while some, like black pepper oleoresin, also offer preservative qualities.

Beyond the culinary world, spice oleoresins find significant application in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. They are incorporated into a variety of medicines and health supplements, not only to mask unpleasant tastes or provide appealing aromas but also for their inherent medicinal properties. For instance, black pepper oleoresin is a component in traditional Indian medicinal systems like Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani, used for addressing various ailments. Similarly, cardamom oleoresin is recognised for its benefits in treating digestive issues. Their use extends to formulations designed to address specific illnesses, and as active ingredients in carminative, stomachic, and stimulant preparations.
Moreover, the cosmetics and personal care industry in India increasingly utilises spice oleoresins. They are valued for their natural fragrances and potential skin benefits, finding their way into products like creams, soaps, shampoos, and perfumes. This trend is driven by a growing consumer preference for natural and herbal ingredients in their personal care routines. The fragrance industry also leverages oleoresins for their rich and true-to-origin scent profiles in products such as air fresheners and specialised perfumes. Finally, the animal feed sector indirectly benefits from oleoresin extraction, as the residual spice powder, rich in nutrients, can be used in animal feed formulations, contributing to improved animal performance and productivity. While the direct use of oleoresins in Indian household cooking is still evolving, their integral role in the organised food processing sector means they are a substantial, albeit often unseen, presence in the modern Indian kitchen through processed foods and ready-to-use products.




F*ckin’ awesome issues here. I’m very satisfied to see your post. Thanks so much and i am taking a look ahead to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
This is a very good tips especially to those new to blogosphere, brief and accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
I like this blog very much so much fantastic information.
Hey! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this page to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
Nice post. I learn one thing more difficult on totally different blogs everyday. It’ll always be stimulating to learn content from different writers and apply a little one thing from their store. I’d prefer to use some with the content material on my blog whether or not you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a link on your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
Merely a smiling visitor here to share the love (:, btw great layout.
Just wanna input on few general things, The website layout is perfect, the written content is really wonderful : D.
Very fantastic info can be found on blog.
Hello my friend! I want to say that this article is amazing, nice written and include approximately all vital infos. I would like to see more posts like this.
I have been checking out many of your articles and i can claim pretty good stuff. I will definitely bookmark your blog.
very nice submit, i certainly love this website, carry on it
Well I sincerely liked studying it. This article provided by you is very helpful for good planning.
Hey! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
Pretty component to content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to assert that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your weblog posts. Any way I will be subscribing for your feeds and even I achievement you get admission to constantly quickly.
Wonderful post but I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit further. Thank you!
Hello! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I genuinely enjoy reading through your blog posts. Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that go over the same topics? Thanks a ton!
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It really useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and aid others like you helped me.
Regards for helping out, good information.
Nice blog here! Also your site a lot up very fast! What web host are you using? Can I am getting your associate link to your host? I want my website loaded up as fast as yours lol
Some truly tremendous work on behalf of the owner of this website , perfectly outstanding subject matter.
Very superb visual appeal on this web site, I’d rate it 10 10.
Enjoyed studying this, very good stuff, appreciate it.
As I website possessor I believe the content here is very good, thanks for your efforts.
Howdy! Would you mind if I share your blog with my facebook group? There’s a lot of people that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Thanks
I have learn a few excellent stuff here. Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much effort you set to create such a wonderful informative website.
Hello! I just would like to give a huge thumbs up for the great info you have here on this post. I will be coming back to your blog for more soon.
Wonderful work! This is the type of info that should be shared around the web. Shame on Google for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my site . Thanks =)
Your home is valueble for me. Thanks!…
Some genuinely great blog posts on this internet site, thanks for contribution. “Gratitude is merely the secret hope of further favors.” by La Rochefoucauld.
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I have truly enjoyed browsing your blog posts. After all I will be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again soon!
You have brought up a very wonderful details, appreciate it for the post.
Great V I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs and related information ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, website theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Nice task..
I like this web site so much, saved to favorites. “Respect for the fragility and importance of an individual life is still the mark of an educated man.” by Norman Cousins.
I consider something truly interesting about your weblog so I saved to my bookmarks.
I real pleased to find this web site on bing, just what I was looking for : D as well saved to favorites.
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! By the way, how can we communicate?
Good write-up, I?¦m normal visitor of one?¦s site, maintain up the nice operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
What¦s Taking place i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It positively helpful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to give a contribution & assist other users like its helped me. Great job.
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share. Kudos!
The next time I learn a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I imply, I do know it was my option to read, however I really thought youd have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you may repair should you werent too busy in search of attention.
naturally like your web site however you need to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very bothersome to tell the truth nevertheless I’ll definitely come again again.
You have brought up a very good points, thankyou for the post.
I love meeting utile information , this post has got me even more info! .
Greetings from Idaho! I’m bored to death at work so I decided to check out your blog on my iphone during lunch break. I love the info you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m shocked at how quick your blog loaded on my mobile .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, superb blog!
Thank you for sharing with us, I think this website really stands out : D.
I have read several good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how much effort you put to make such a magnificent informative web site.
naturally like your web site but you need to test the spelling on several of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling issues and I to find it very troublesome to tell the reality then again I¦ll definitely come again again.
I like this web blog very much, Its a really nice post to read and find info .
Hello.This post was extremely fascinating, especially since I was investigating for thoughts on this subject last Tuesday.
F*ckin’ remarkable things here. I’m very glad to see your post. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
I got good info from your blog
Some genuinely good info , Sword lily I noticed this.
I’ve read several good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much effort you put to make such a great informative site.
I got what you intend, thanks for posting.Woh I am happy to find this website through google.
F*ckin’ remarkable things here. I am very glad to see your post. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
Hi, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, fantastic blog!
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You obviously know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your blog when you could be giving us something enlightening to read?
Spot on with this write-up, I truly think this web site wants much more consideration. I’ll most likely be again to learn much more, thanks for that info.
I¦ve learn some good stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how much effort you put to create one of these great informative website.
whoah this blog is fantastic i really like reading your articles. Stay up the good paintings! You already know, a lot of people are hunting round for this information, you can help them greatly.
I really like your writing style, fantastic info, thanks for putting up :D. “Much unhappiness has come into the world because of bewilderment and things left unsaid.” by Feodor Mikhailovich Dostoyevsky.
Yesterday, while I was at work, my cousin stole my apple ipad and tested to see if it can survive a 25 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My iPad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is entirely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I have truly loved browsing your blog posts. After all I will be subscribing to your rss feed and I am hoping you write once more very soon!
I like this blog very much, Its a very nice berth to read and get information.
I believe other website proprietors should take this site as an model, very clean and superb user pleasant design and style.
USA Flights 24 — search engine helps you compare prices from hundreds of airlines and travel sites in seconds — so you can find cheap flights fast. Whether you’re planning a weekend getaway, a cross-country adventure, or an international vacation, we make it easy to fly for less.
Those are yours alright! . We at least need to get these people stealing images to start blogging! They probably just did a image search and grabbed them. They look good though!
My husband and i were quite thrilled Edward could deal with his research via the precious recommendations he obtained out of your web site. It is now and again perplexing just to choose to be freely giving guides which some other people may have been trying to sell. And now we consider we need the writer to be grateful to for this. These explanations you made, the straightforward blog navigation, the relationships you make it possible to promote – it’s got many spectacular, and it’s letting our son and our family recognize that that topic is thrilling, and that is wonderfully mandatory. Thank you for the whole thing!
Great write-up, I am normal visitor of one’s site, maintain up the excellent operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
NuStar Game highlights a platform experience centered on usability and performance. With a streamlined layout and responsive design, the platform allows users to explore available features easily while maintaining stable performance on both desktop and mobile devices.
Good write-up, I¦m regular visitor of one¦s site, maintain up the excellent operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thanks, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your web site?